Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Showing 1–24 of 47 results
-
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
8085 Microprocessor In-Built Power Supply
The 8085 Microprocessor requires a built-in power supply of +5V DC for its operation. It follows TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) compatibility, meaning that all its voltage levels are based on TTL standards.
SKU: DSS-00101 -
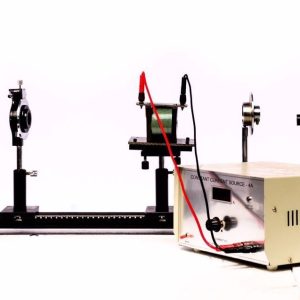
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
B-H Curve Apparatus
The B-H Curve Apparatus is a device used to study the magnetization characteristics of ferromagnetic materials by plotting their hysteresis (B-H) curve. This curve represents the relationship between magnetic flux density (B) and magnetic field strength (H) in a material, helping to analyze properties like coercivity, retentivity, and permeability.
SKU: DSS-00103 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Ballistic Galvanometer
A Ballistic Galvanometer is a highly sensitive electrical instrument used to measure small quantities of charge and impulse currents. Unlike a regular galvanometer, which measures steady currents, a ballistic galvanometer is designed to respond to sudden pulses of current and is primarily used for experiments related to electromagnetic induction and capacitance measurement.
SKU: DSS-00104 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Bending of Beam Apparatus (Using Koeing`s Method)
The Bending of Beam Apparatus using Koenig’s Method is a setup used to determine the Young’s Modulus (E) of a beam material. This method involves placing a beam on two supports and applying a known load at the center or at two equidistant points, then measuring the resulting deflection.
SKU: DSS-00107 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Bifilar Pendulum
A bifilar pendulum is a mechanical system used to study rotational motion and moment of inertia. It consists of a rigid body (a bar or disc) suspended by two parallel strings or wires, allowing it to oscillate in a horizontal plane. The plate is suspended by means of two strings of equal lengths from a rigid suspended (i.e. a heavy T-shaped clamp with two split chuck is provided on the heavy base). It consists of a heavy cast iron rectangular plate of dimension 15x10x1.5cm. When the plate is suspended freely, the two strings will be equally inclined to the horizontal face of the plate. The plate has six holes two holes on top, two holes on the front side and two holes on the third side of the top.
SKU: DSS-00108 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Brewester Angle Apparatus
Brewster’s Angle Apparatus is designed to study the Brewster’s angle phenomenon and the polarization of reflected light. The essential elements of the apparatus consist of a goniometer, a laser light source capable of projecting a light beam that is linearly polarized in its plane of incidence, and a pinhole photodetector with an output measurement unit for detecting and measuring the intensity of light reflected. The diode laser and polarizer rotator are mounted on an optical rail.
SKU: DSS-00109 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Carey – Foster Bridge
The Carey Foster bridge is a bridge circuit used to measure medium resistances or to measure small differences between two large resistances. It was invented by Carey Foster as a variant on the Wheatstone Bridge. It is also used for accurately measuring small differences in resistance. It is especially useful for determining the resistance per unit length of a wire and measuring low resistances with high precision.
SKU: DSS-00110 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Cavendish Pendulum
The core of the apparatus is a torsion pendulum made of a light bar with two small lead spheres, which is suspended horizontally from a thin wire. The apparatus is moved from its rest position by the attraction of the two spheres to two larger lead spheres. When the two large spheres are rotated to a new position, the torsion balance will vibrate about a new rest position. The rotary motion is measured using a capacitive differential sensor, which largely suppresses noise and vibration components in the signal. The output is then recorded using a computer. For subsequent evaluation, the data can be exported to a spreadsheet. Alternatively, the motion can be demonstrated with the aid of a light pointer.
SKU: DSS-00111 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Compound Pendulum (Steel C.P.)
Compound Pendulum (Steel C.P.) is a rigid body that oscillates about a horizontal axis under the influence of gravity. Unlike a simple pendulum, which consists of a mass suspended by a string, a compound pendulum has distributed mass and can be made from materials such as steel for higher rigidity and durability.
SKU: DSS-00112 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Coulomb`s Law Demonstrator
A Coulomb’s Law Demonstrator is a scientific apparatus used to verify Coulomb’s Law, which describes the electrostatic force between two charged objects. It helps visualize how the force between two charges varies with distance and magnitude.
SKU: DSS-00113 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Driven Damped Harmonic Oscillations Experiment
A Driven Damped Harmonic Oscillations Experiment investigates the behavior of a harmonic oscillator under the influence of an external driving force and damping. This experiment is fundamental in physics and engineering, as it models real-world systems like mechanical vibrations, electrical circuits, and molecular oscillations.
SKU: DSS-00114 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
e/m Helical Method
The Helical Method is an experimental technique used to determine the charge-to-mass ratio (e/me/m) of an electron by observing its motion in a uniform magnetic field. This method is based on the principle that a charged particle moving perpendicular to a magnetic field follows a circular or helical trajectory due to the Lorentz force.
SKU: DSS-00115 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
e/m Thomson Method Apparatus
The Thomson Method is one of the earliest and most direct methods for determining the charge-to-mass ratio (e/me/m) of an electron. This method uses the deflection of an electron beam under the influence of electric and magnetic fields.
SKU: DSS-00116 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Earth Inductor
The Earth Inductor is a device used to measure the Earth’s magnetic field based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It consists of a coil that, when rotated in the Earth’s magnetic field, induces an electromotive force (EMF) due to the change in magnetic flux.
SKU: DSS-00118 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Faraday Rotation Setup
Faraday Rotation is the rotation of the plane of polarization of light when it passes through a material under the influence of a magnetic field. This effect, discovered by Michael Faraday in 1845, is used in optical isolators, magneto-optical devices, and studies of magnetism in materials.
SKU: DSS-00120 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Fly Wheel Moment of Inertia
Fly Wheel Moment of Inertia for Rotational Motion Comprising of carefully machined and balanced cast iron wheel of about 8“ dia and 4.4cm thick, and steel spindle supported on the ball bearings in strong iron brackets. The sides of the wheel are red or grey painted. The top of wheel is chrome plated and is marked with a thick red line. A pointer is fixed to one of the brackets. Diametric hole is drilled in the shaft to take a pin and cord. The base is provided with four holes so that the apparatus can be fixed on a wall, complete with cord and hook. Setup Contains:- Fly Wheel Unit 8 Inch, Digital Stop Watch, Vernier Calliper, Slotted Weight 250gm & Inch Tape. Comprising of carefully machined and balanced cast iron wheel of about 8“ dia and 4.4cm thick, and steel spindle supported on the ball bearings in strong iron brackets. The sides of the wheel are red or grey painted. The top of wheel is chrome plated and is marked with a thick red line. A pointer is fixed to one of the brackets. Diametric hole is drilled in the shaft to take a pin and cord. The base is provided with four holes so that the apparatus can be fixed on a wall, complete with cord and hook. Setup Contains:- Fly Wheel Unit 8 Inch, Digital Stop Watch, Vernier Calliper, Slotted Weight 250gm & Inch Tape.
SKU: DSS-00158 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Four Probe Method Setup
The Four Probe Method is used to accurately measure the resistivity of semiconductors and thin films by eliminating the effects of contact resistance. It is widely used for materials with high resistivity, such as silicon and germanium.
SKU: DSS-00123 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
Fresnel`s Bi-prism
Fresnel’s Bi-Prism is an optical device that produces two coherent sources from a single light source, leading to an interference pattern similar to Young’s Double-Slit Experiment. It consists of a thin bi-prism (two prisms joined at their bases), which creates two virtual sources of light.
SKU: DSS-00125 -
Physics Laboratory Equipment (Applied Mech)
GM Counter Experiment
A Geiger-Müller (GM) counter is a radiation detector used to measure ionizing radiation (alpha, beta, and gamma rays). It consists of a gas-filled tube that detects radiation through ionization.
The GM tube operates on the principle that when radiation passes through it, it ionizes the gas inside, producing an electrical pulse that is counted.
SKU: DSS-00121 -
-